- +91-8052038976
- drrishishukla@gmail.com
- SWAROOP NAGAR, KANPUR 208002
Diabetes Tests

Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy
Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy is a serious complication of Diabetes. The test is done to check the involvement of involuntary part of heart due to diabetes.
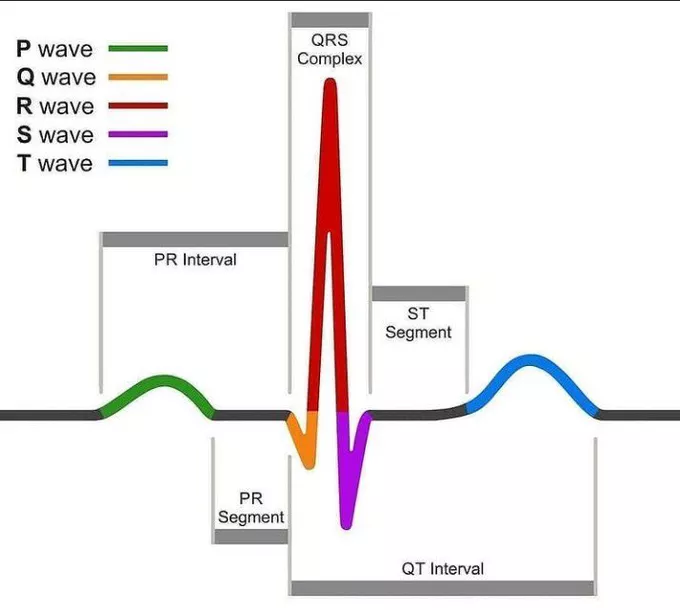
Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiogram is a written record of a heartbeat, while electrocardiograph is an instrument with which it is recorded. This test is done to check the normality/abnormality of the heartbeat.
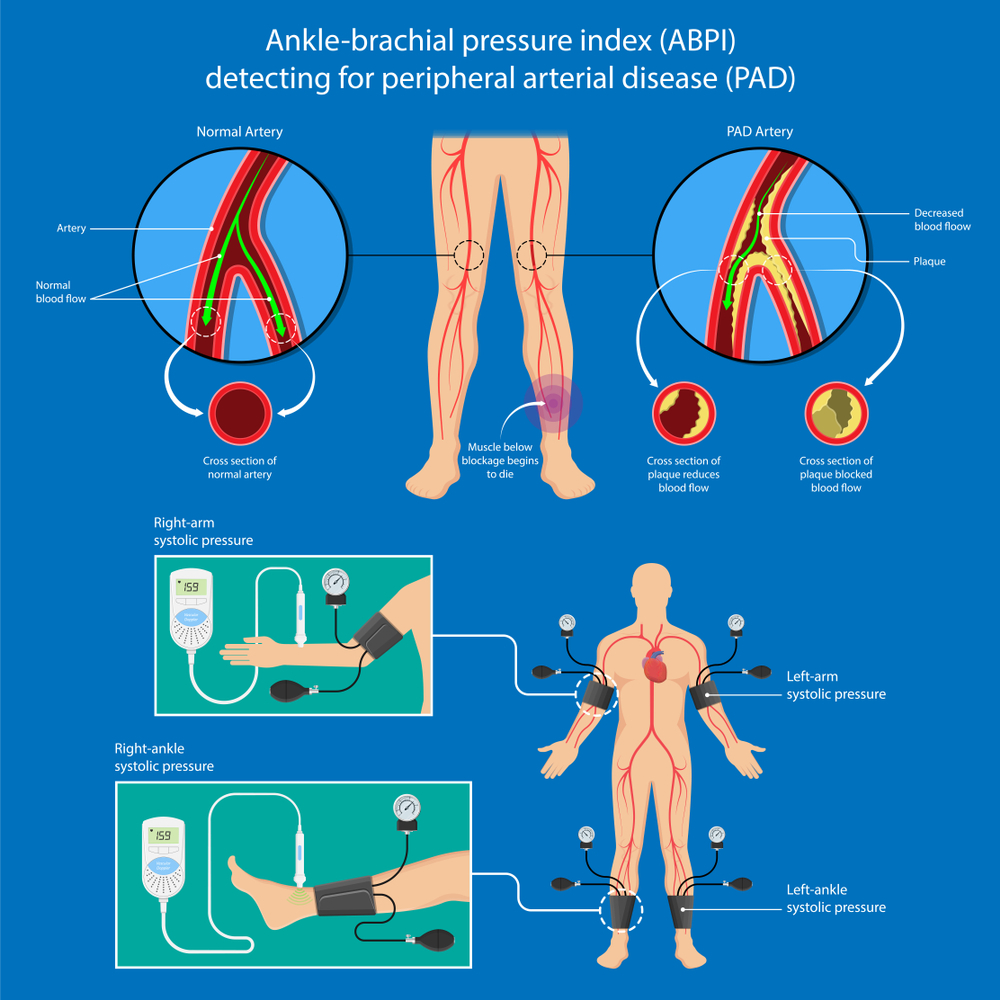
Ankle Brachial Index (ABI)
This test is done to check the blood flow (arterial) in lower limbs. It is very strongly correlated with heart disease and stroke.
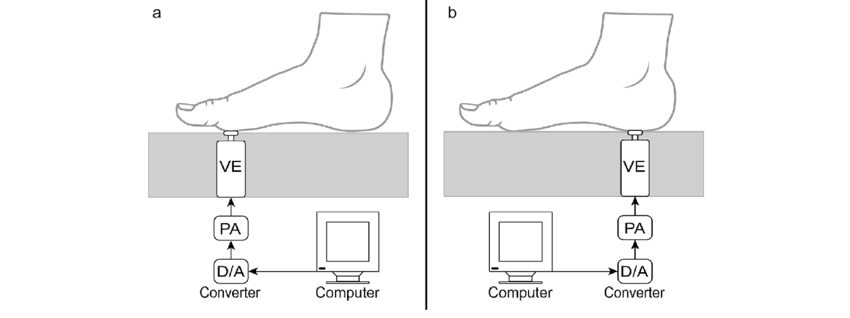
vibration perception threshold (VPT)
Use of the vibration perception threshold (VPT) is a simple way of detecting large-fiber dysfunction, thus identifying individuals with diabetes at risk of ulceration.
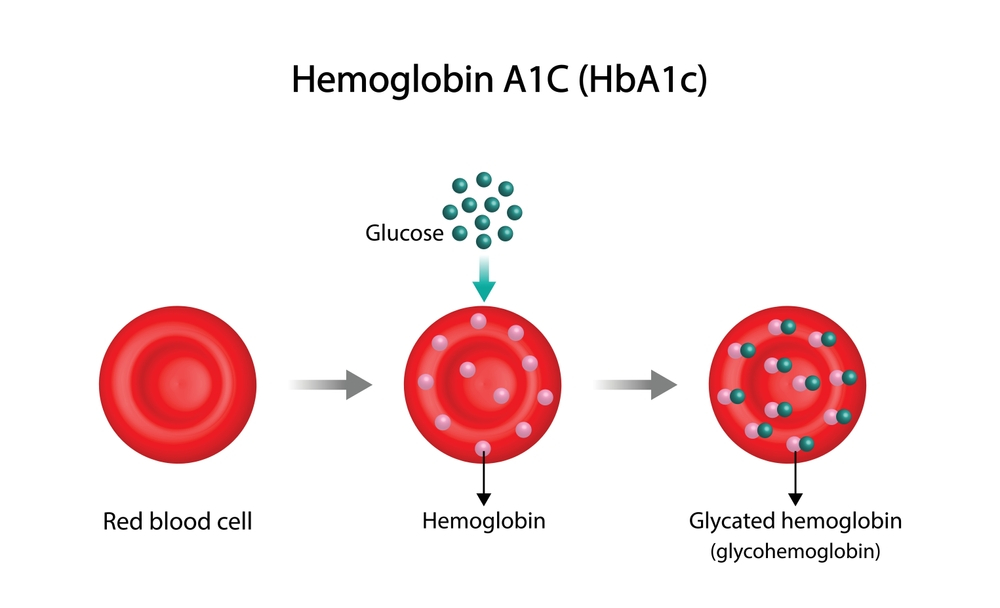
Glycosylated Haemoglobin (HBAIC) Spot Report
A high HbA1c means you have too much sugar in your blood. This means you are more likely to develop diabetes complications, like serious problems with your eyes and feet. Why it is done-earlier there were only 2 major readings to get the status of Glucose level in the body – FPG and PPG but HBA1C is the perfect way of knowing the average sugar levels of 3 months in the body which helps Consultants to manage your diabetes in better way.
Foot Print (FP)
It is the impression of feet which indicates unusual pressure in feet. Patient having unusual pressure on feet is prone to have infections.
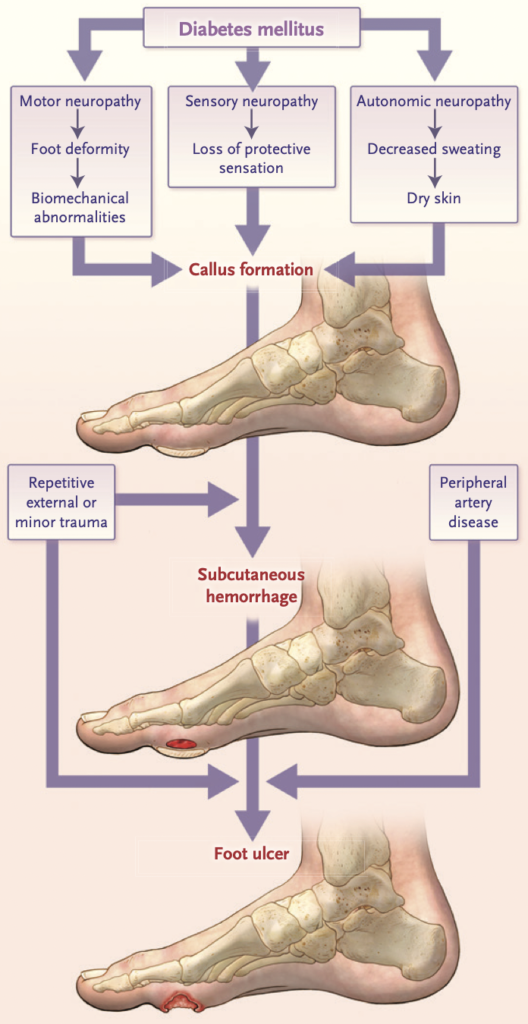

Urine Microalbumin
A urine microalbumin test is a test to detect very small levels of a blood protein (albumin) in your urine. A microalbumin test is used to detect early signs of kidney damage in people who are at risk of developing kidney disease.
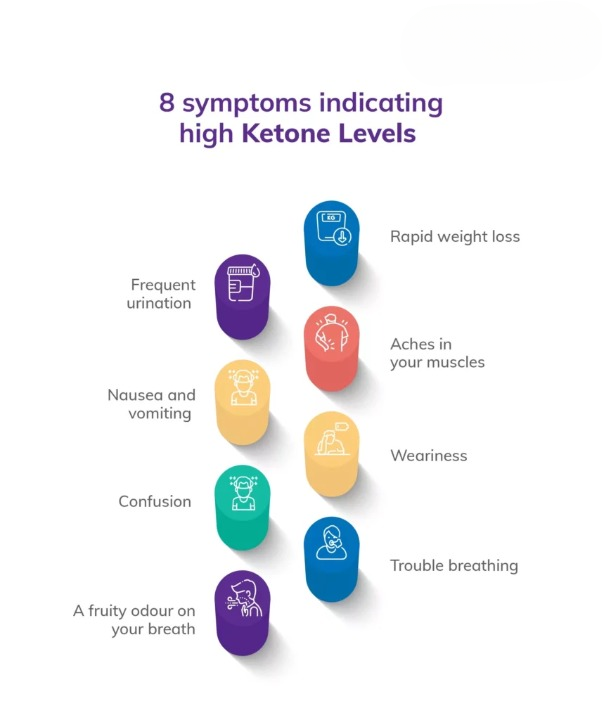
Urine Ketones (URINE R)
If your cells don’t get enough glucose, your body burns fat for energy instead. This produces a substance called ketones, which can show up in your blood and urine. High ketone levels in urine may indicate diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a complication of diabetes that can lead to coma or even death. ketones in urine test can prompt you to get treatment before a medical emergency occurs.
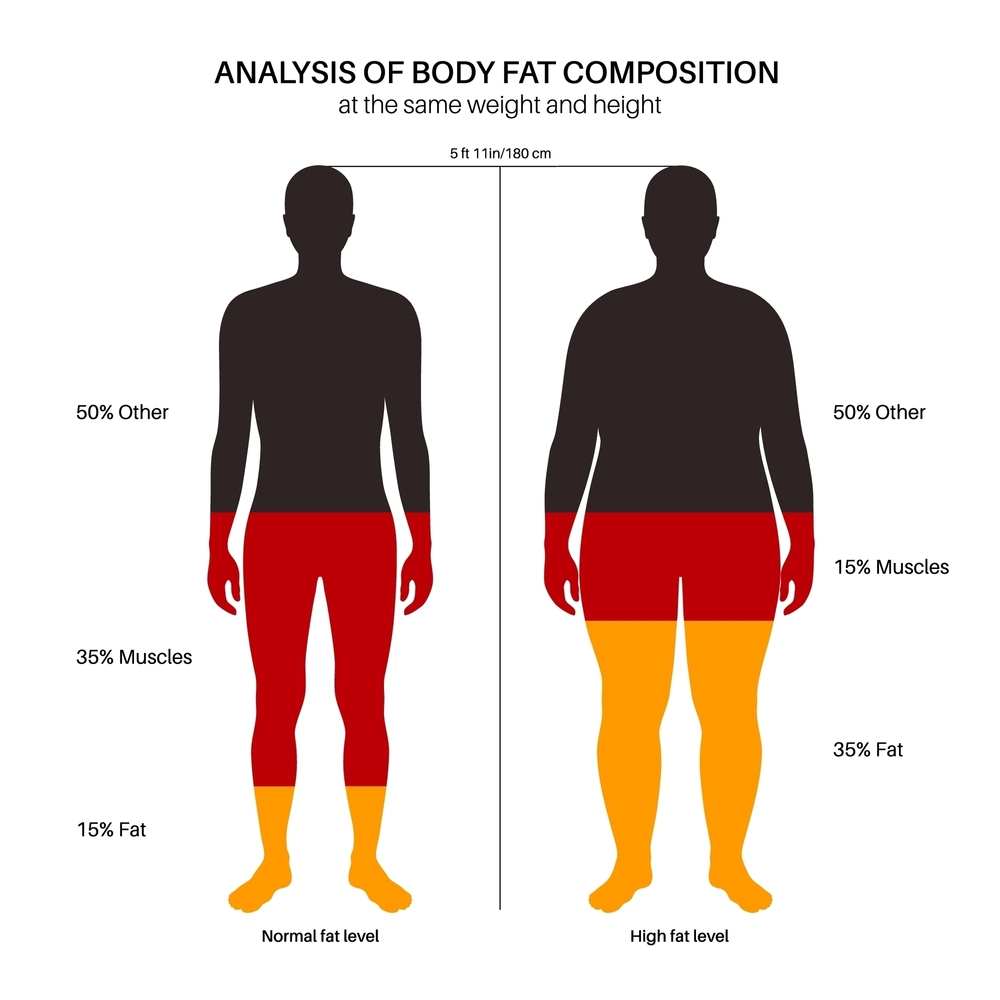
Body Composition Analysis (BCA)
The test tells about total body fat present in the patient’s body and it specially detects the visceral fat. Visceral fat is dangerous for the body and it accumulates mostly in and around our abdomen.
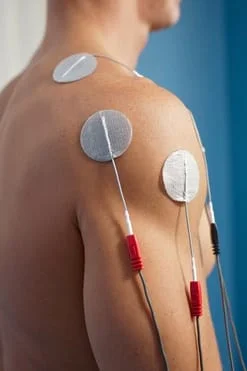
Interferential current therapy
Interferential current therapy is an effective therapy option used by many physiotherapy clinics to relieve pain and accelerate the self-healing process,getting your body back to a healthy, pain free state. The high frequency signals of an IFC penetrate through the skin into deeper lying muscle tissues.
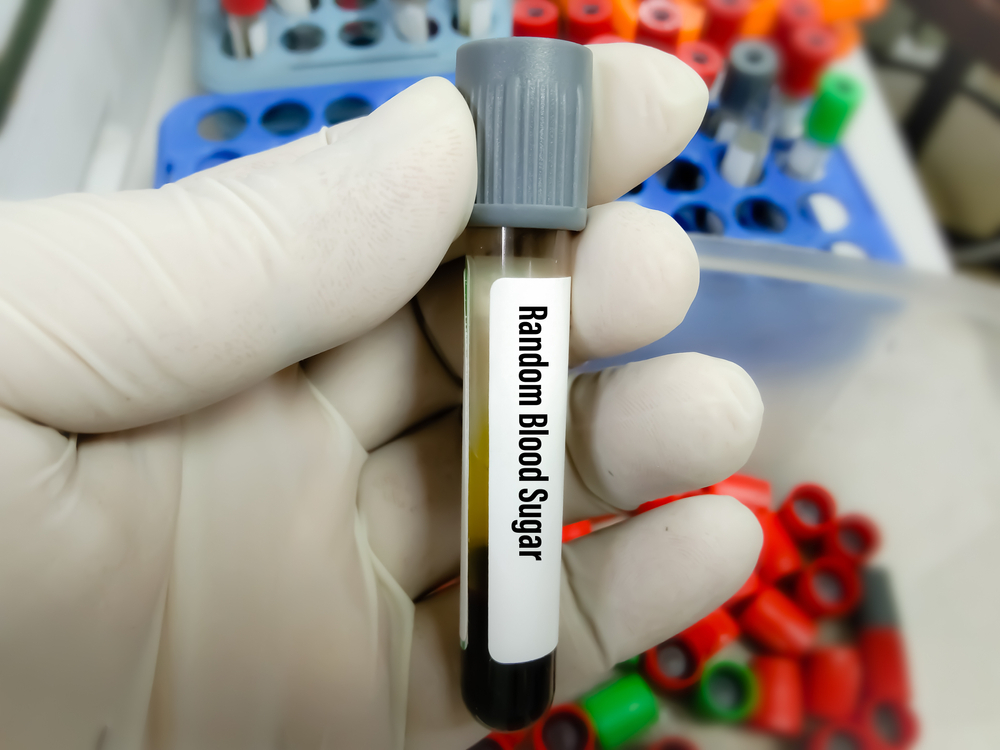
random blood sugar
A random blood sugar test checks your blood glucose at a random time of day. A level of 200 mg/dl or higher is a sign that you have diabetes.
fundus Imaging
A fundus Imaging or retinal imaging is a specialized low power microscope with an attached camera designed to photograph the interior surface of the eye, including the retina, retinal vasculature, optic disc, macula and posterior pole.
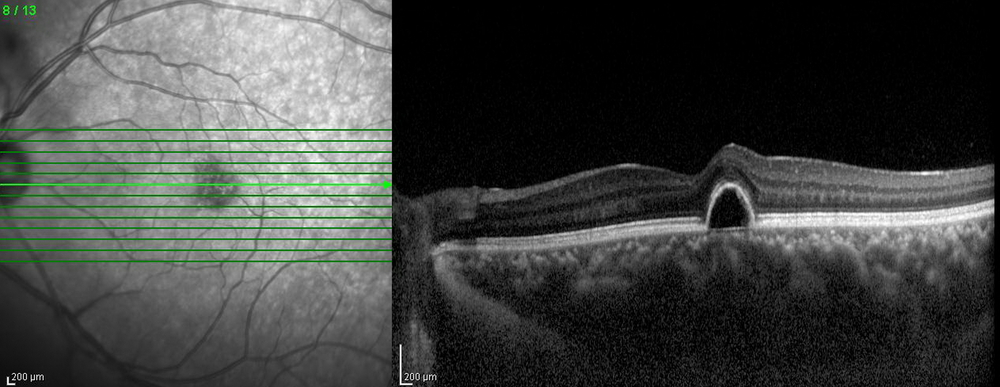
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
OCT is a non-invasive imaging test. OCT uses light waves to take cross-section pictures of your retina. With OCT, your ophthalmologist can see each of the retina’s distinctive layers. This allows your ophthalmologist to map and measure their thickness.
Ambulatory Glucose Profile
Ambulatory Glucose Profile (AGP) is a single page, standardized report for interpreting a patient’s daily glucose and insulin patterns. AGP provides both graphic and quantitative characterizations of daily glucose patterns. The first version included a glucose median and interquartile ranges graphed as a 24 hour day. It records blood sugar at time interval of every 15 minutes for 2 weeks and produces nice graphs.
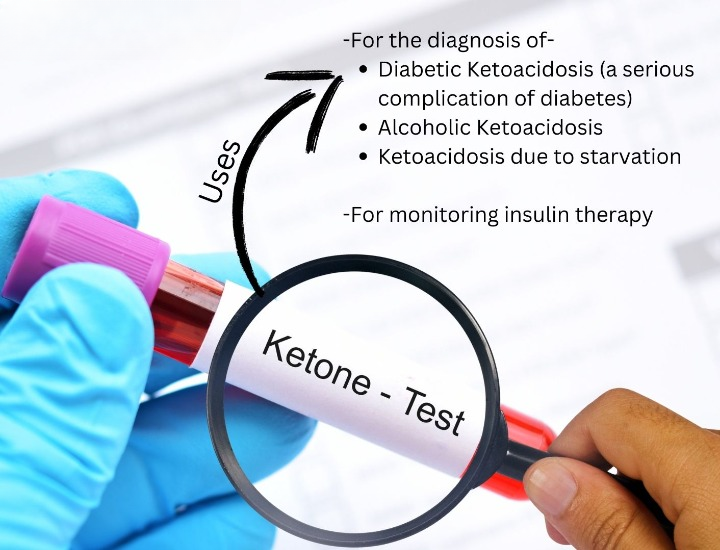
Blood Ketones
Ketones or ketone bodies are by-products of fat metabolism. This test measures the number of ketones in the blood. Ketones are produced when glucose is not available to the body’s cells as an energy source and/or when the body cannot use glucose as a fuel source because there is no insulin or not enough insulin. It indicates insulin deficiency. Values more than 0.6 nmol/L is indicative of severe insulin deficiency and is an emergency situation.
If you need urgent care, simply call our 24 hour emergency hotline.
Your personal case manager will ensure that you receive the best possible care.
Call Now